Juan J. Sánchez
Sponsor

USMLE Step 2 CK
Days Left: 0
What is it

The second most terrifying test in my career (the first one being the USMLE Step 1).
Step 2 assesses whether you can apply medical knowledge, skills, and understanding of clinical science essential for the provision of patient care under supervision and includes emphasis on health promotion and disease prevention. Step 2 ensures that due attention is devoted to principles of clinical sciences and basic patient-centered skills that provide the foundation for the safe and competent practice of medicine.
How long is it

Nine hours long.
Step 2 CK is a one-day examination. The test items are divided into blocks, and test item formats may vary within each block.
The number of items in a block will be displayed at the beginning of each block. This number will vary among blocks, but will not exceed 45 items. The total number of items on the overall examination form will not exceed 355 items. Regardless of the number of items, 60 minutes are allotted for the completion of each block.
On the test day, examinees have a minimum of 45 minutes of break time and a 15- minute optional tutorial. The amount of time available for breaks may be increased by finishing a block of test items or the optional tutorial before the allotted time expires.
What subjects does it test

Internal Medicine, Pediatric, Surgery, Psychiatry, Ethics, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, and Obstetrics and Gynecology.
For a full content description, open the spoiler.
1. General Principles
Infancy and Childhood
Adolescence
Senescence
Medical Ethics and Jurisprudence
Applied Biostatistics and Clinical Epidemiology
Systems-Based Practice and Patient Safety
2. Infectious and Parasitic Diseases
3. Neoplasms
4. Immunologic Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
5. Diseases of the Blood and Blood-forming Organs
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
6. Mental Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
7. Diseases of the Nervous System and Special Senses
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
8. Cardiovascular Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
9. Diseases of the Respiratory System
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
10. Nutritional and Digestive Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
11. Gynecologic Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
12. Renal, Urinary, and Male Reproductive Systems
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
13. Disorders of Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Puerperium
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
14. Disorders of the Skin and Subcutaneous Tissues
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
15. Diseases of the Musculoskeletal System and Connective Tissue
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
16. Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
Mechanisms of Disease
Diagnosis
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
17. Congenital Anomalies
18. Conditions Originating in the Perinatal Period
19. Symptoms, Signs, and Ill-defined Conditions
20. Injury and Poisoning
Infancy and Childhood
- Normal growth and development
Adolescence
- Sexuality; separation from parents/autonomy; physical changes of puberty
Senescence
- Normal physical and mental changes associated with aging
Medical Ethics and Jurisprudence
- Consent and informed consent to treatment (eg, full disclosure, alternate therapies, risks and benefits, life-support, advance directives, health care proxy) and research issues (eg, consent, placebos, conflict of interest, vulnerable populations)
Physician-patient relationship (eg, truth-telling, confidentiality, privacy, autonomy, public reporting) and birth-related issues (eg, prenatal diagnosis, abortion, maternal-fetal conflict)
Death and dying (eg, diagnosing death, organ donation, euthanasia, physician-assisted suicide) and palliative care (eg, hospice, pain management, family counseling, psychosocial and spiritual issues, fear and loneliness)
Applied Biostatistics and Clinical Epidemiology
- Understanding statistical concepts of measurement in medical practice
Interpretation of the medical literature
Systems-Based Practice and Patient Safety
- Systems-based practice and quality improvement (microsystems and teams including hand-offs, standardization of processes, reducing deviance)
Patient safety, medical errors and near misses (sentinel events, problem identification, root cause analysis)
2. Infectious and Parasitic Diseases
3. Neoplasms
4. Immunologic Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
- Anaphylaxis and other allergic reactions
HIV infection/AIDS
Immunization against infectious agents (including infants, children, adults, the elderly; patients having compromised immune systems)
Mechanisms of Disease
- Abnormalities of cell-mediated immunity
Abnormalities of humoral immunity
Diagnosis
- Anaphylactic reactions and shock
Connective tissue disorders (eg, mixed connective tissue disease and systemic lupus erythematosus)
HIV infection/AIDS; deficiencies of cell-mediated immunity
Deficiencies of humoral immunity; combined immune deficiency
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
5. Diseases of the Blood and Blood-forming Organs
Health and Health Maintenance
- Anemia (iron deficiency, vitamin-related, drug-induced, sickle cell)
Infection(systemic)
Mechanisms of Disease
- Red cell disorders
Coagulation disorders
White cell disorders, including leukopenia, agranulocytosis, and neoplasms
Diagnosis
- Anemia, disorders of red cells, hemoglobin, and iron metabolism (eg, blood loss; iron deficiency anemia, nutritional deficiencies; pernicious anemia, other megaloblastic anemias; hemolytic anemia; anemia associated with chronic disease; aplastic anemia, pancytopenia; thalassemia; sickle cell disease; polycythemia vera; hemochromatosis)
Bleeding disorders, coagulopathies, thrombocytopenia (eg, hemophilia, von Willebrand disease; qualitative and quantitative platelet deficiencies; disseminated intravascular coagulation; hypofibrinogenemia; immune thrombocytopenic purpura; hemolytic-uremic syndrome)
Neoplastic disorders (eg, Hodgkin disease, non-Hodgkin lymphomas; acute leukemia in children; acute leukemia in adults; chronic leukemic states; mycosis fungoides; multiple myeloma)
Eosinophilia and reactions to transfusion of blood components (including complications) and leukopenic disorders, agranulocytosis
Infection (eg, sepsis, malaria, mononucleosis)
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
6. Mental Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
- Early identification and intervention (eg, suicide potential, depression, alcohol/substance abuse, family involvement in schizophrenia)
Mechanisms of Disease
- Biologic markers of mental disorders and mental retardation syndromes
Intended/unintended effects of therapeutic interventions, including effects of drugs on neurotransmitters
Diagnosis
- Mental disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence (eg, mental retardation; communication disorders; pervasive developmental disorders; attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; disruptive disorders; tic disorders; elimination disorders)
Substance-related disorders (eg, alcohol and other substances)
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
Mood disorders (eg, bipolar disorders; major unipolar depressive disorders; dysthymic disorder; mood disorder due to a general medical condition; medication-induced mood disorder)
Anxiety disorders (eg, panic disorder; phobia; obsessive-compulsive disorder; post-traumatic stress disorder; generalized anxiety disorder; acute stress disorder; separation anxiety disorder; anxiety due to a general medical condition; substance-induced anxiety disorder)
Somatoform disorders (eg, factitious disorder; somatization disorder; pain disorder; conversion disorder; hypochondriasis)
Other disorders/conditions (eg, sexual and gender identity disorders; personality disorders; child, spouse, elder abuse; eating disorders; adjustment disorders; dissociative disorders; psychological factors affecting medical conditions)
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
7. Diseases of the Nervous System and Special Senses
Health and Health Maintenance
- Cerebrovascular disease, cerebral infarction
Nutritional deficiencies, toxic injuries, and occupational disorders including lead, carbon monoxide, and organophosphate poisoning
Infection involving the nervous system, eyes, or ears
Degenerative and demyelinating disorders, including Alzheimer disease and multiple sclerosis
Mechanisms of Disease
- Localizing anatomy:
- brain and special senses
brain stem
spinal cord
neuromuscular system
Increased intracranial pressure and altered state of consciousness
Infection
Degenerative/developmental and metabolic disorders - brain and special senses
Diagnosis
- Disorders of the eye (eg, blindness; glaucoma; infection; papilledema; optic atrophy; retinal disorders; diabetic retinopathy; diplopia; cataract; neoplasms; vascular disorders; uveitis; iridocyclitis; traumatic, toxic injury; toxoplasmosis)
Disorders of the ear, olfaction, and taste (eg, deafness, hearing loss, otitis, mastoiditis; vertigo, tinnitus, Meniere disease; acoustic neuroma; traumatic, toxic injury)
Disorders of the nervous system:- paroxysmal disorders (eg, headache; trigeminal neuralgia; seizure disorders; syncope)
cerebrovascular disease (eg, intracerebral hemorrhage; ischemic disorders; aneurysm, subarachnoid hemorrhage; cavernous sinus thrombosis)
traumatic, toxic injury; including lead, carbon monoxide, and organophosphate poisoning
infections (eg, bacterial, fungal, viral, opportunistic infection in immunocompromised patients; Lyme disease; abscess; neurosyphilis; Guillain-Barr syndrome)
neoplasms (eg, primary; metastatic; neurofibromatosis)
metabolic disorders (eg, metabolic encephalopathy, vitamin B12 [cobalamin] deficiency, vitamin B1 [thiamine] deficiency; coma, confusion, delirium, dementia)
degenerative and developmental disorders (eg, Alzheimer disease; Huntington disease; parkinsonism; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; Tay-Sachs disease; multiple sclerosis; cerebral palsy; dyslexia)
neuromuscular disorders, gait abnormalities, and disorders relating to the spine and spinal nerve roots (eg, myasthenia gravis; muscular dystrophy; peripheral neuropathy; neck pain; cervical radiculopathy; lumbosacral radiculopathy; spinal stenosis)
sleep disorders (eg, narcolepsy, idiopathic hypersomnolence, restless legs syndrome, REM sleep behavior disorder, circadian rhythm sleep disorder, sleep apnea)
- paroxysmal disorders (eg, headache; trigeminal neuralgia; seizure disorders; syncope)
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
8. Cardiovascular Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
- Arterial hypertension
Atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease; hyperlipidemia
Prevention of rheumatic heart disease, thromboembolic disease, pulmonary emboli, bacterial endocarditis
Mechanisms of Disease
- Cardiac output, resistance, central venous pressure
Valvular stenosis, incompetence
Congenital heart disease
Regulation of blood pressure
Disorders of the arteries and veins
Diagnosis
- Dysrhythmias; palpitations, syncope (eg, premature beats; paroxysmal tachycardias; atrial flutter and fibrillation; bradycardias; ventricular fibrillation; cardiac arrest)
Heart failure (congestive, diastolic, systolic dysfunction), dyspnea, fatigue, peripheral edema of cardiac origin (eg, chronic heart failure; cor pulmonale)
Ischemic heart disease; chest pain of cardiac origin (eg, angina pectoris; coronary insufficiency; myocardial infarction)
Diseases of the myocardium (eg, hypertrophic; myocarditis)
Diseases of the pericardium (eg, acute pericarditis; chronic constrictive pericardiopathy; pericardial effusion; pericardial tamponade)
Valvular heart disease (eg, acute rheumatic fever; mitral and aortic valve disorders; infective endocarditis)
Congenital cardiovascular disease (eg, patent ductus arteriosus; atrial septal defect; ventricular septal defect; endocardial cushion defect; tetralogy of Fallot; coarctation of the aorta)
Systemic hypotension, hypovolemia, cardiogenic shock; cyanosis
Arterial hypertension (eg, essential; secondary)
Atherosclerosis - lipoproteins
Disorders of the great vessels (eg, dissecting aortic aneurysm; ruptured aneurysm; aortoiliac disease)
Peripheral arterial vascular diseases, vasculitis (eg, polyarteritis; temporal arteritis; arteriovenous fistula)
Diseases of the veins, peripheral edema (eg, varicose veins; thrombophlebitis; deep venous thrombosis)
Traumatic injury
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
9. Diseases of the Respiratory System
Health and Health Maintenance
- Chronic bronchitis, asthma, emphysema, carcinoma of the larynx, carcinoma of the lung; pulmonary aspiration, atelectasis; tuberculosis
Mechanisms of Disease
- Ventilatory dysfunction (eg, obstructive disorders: asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis, bronchitis, bronchiectasis, emphysema)
Respiratory failure, acute and chronic, including oxygenation failure (eg, interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, ventilation failure)
Circulatory dysfunction
Neoplastic disorders
Diagnosis
- Disorders of the nose, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, larynx, and trachea (eg, rhinitis; pharyngitis, tonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess; thrush; sinusitis; acute laryngotracheitis; epiglottitis; carcinoma of the larynx; laryngeal/pharyngeal obstruction; trauma; tracheoesophageal fistula)
Infections of the lung (eg, acute bronchiolitis; pneumonia; tuberculosis)
Obstructive airways disease (eg, chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis; asthma, bronchospasm, wheezing; emphysema, ?1-antitrypsin deficiency; cystic fibrosis)
Atelectasis, pulmonary aspiration
Pneumothorax, hemothorax, traumatic injury to the lungs and disorders involving the pleura (eg, pleurisy; pleural effusion)
Pneumoconiosis, fibrosing or restrictive pulmonary disorders (eg, asbestosis; silicosis; sarcoidosis)
Respiratory failure, hypoxia, hypercapnia, dyspnea (eg, respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn; acute respiratory distress syndrome; acute and chronic respiratory failure; drowning)
Pulmonary vascular disorders (eg, pulmonary embolism; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary edema)
Neoplastic disorders of the lungs and pleura (eg, primary tumors; metastatic tumors)
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
10. Nutritional and Digestive Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
- Screening (eg, cancer)
Viral hepatitis and alcohol-related hepatopathy
Mechanisms of Disease
- Malabsorption/malnutrition
Jaundice
Infections/parasites
Obstruction/mechanical
Diagnosis
- Disorders of the mouth, salivary glands, oropharynx, and esophagus (eg, dental disorders; disorders of the salivary glands; esophageal reflux; dysphagia; motility disorders of the esophagus; hiatal hernia; carcinoma of the esophagus)
Disorders of the stomach, small intestine, colon, and rectum/anus (eg, gastritis; peptic ulcer disease; congenital disorders; malabsorption; appendicitis; granulomatous enterocolitis; ischemic colitis; irritable bowel syndrome; diverticula; colonic polyps; ulcerative colitis; peritonitis; bowel obstruction, volvulus, intussusception; hernia; necrotizing enterocolitis; infection; carcinoma of the stomach, colon, and rectum; antibiotic-associated colitis; hemorrhoids; anal fissures; anal fistula; perianal/perirectal abscess)
Disorders of the pancreas (eg, pancreatitis; pseudocyst; carcinoma of the pancreas)
Disorders of the liver and biliary system (eg, hepatitis; cirrhosis; hepatic failure, hepatic encephalopathy, jaundice; portal hypertension; ascites, esophageal varices; cholelithiasis; cholecystitis; hepatic abscess, subphrenic abscess; neoplasms of the liver; storage diseases; neoplasms of the biliary tract)
Traumatic injury and poisoning (including drain cleaner ingestion)
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
11. Gynecologic Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
- Postmenarchal/reproductive
Peri/postmenopausal
Mechanisms of Disease
- Infections (eg, vulvovaginitis; pelvic inflammatory disease; toxic shock; sexually transmitted disease; endometritis; urethritis; Bartholin gland abscess; abscess of the breast; mastitis)
Urinary incontinence and obstruction
Menstrual and endocrinologic disorders; infertility
Diagnosis
- Pelvic relaxation and urinary incontinence (eg, urinary tract infection; uterovaginal prolapse; cystocele, rectocele, urethrocele)
Neoplasms (eg, cervical dysplasia, cancer; leiomyomata uteri; endometrial cancer; ovarian neoplasms; neoplastic disorders of the breast; vulvar neoplasms)
Benign conditions of the breast
Menstrual and endocrinologic disorders (eg, amenorrhea [including undiagnosed pregnancy]; abnormal uterine bleeding; dysmenorrhea; menopausal, postmenopausal disorders [osteoporosis]; premenstrual syndrome; hirsutism, virilization; ovarian disorders [ovarian failure, polycystic ovarian syndrome])
Sexual abuse and rape
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
12. Renal, Urinary, and Male Reproductive Systems
Health and Health Maintenance
- Infection (eg, urinary tract, sexually transmitted diseases [male])
Acute and chronic renal failure including risk factors and prevention and methods of limiting progression
Male health maintenance examination (eg, testicular, prostatic)
Mechanisms of Disease
- Disorders of the male reproductive system
Urinary incontinence and obstruction, enuresis
Renal insufficiency/failure
Electrolyte and water metabolism and acid-base balance
Diagnosis
Disorders of the male reproductive system (eg, infections; torsion of the testis; undescended testicle; neoplasms of the testis; benign prostatic hyperplasia; carcinoma of the prostate; hypospadias; hydrocele, varicocele; urethral stricture, impotence, premature ejaculation)
Disorders of the urinary bladder and urinary collecting system (eg, cystitis; pyelitis; dysuria, hematuria, pyuria; carcinoma of the bladder; urolithiasis; ureteral reflux; neurogenic bladder; urinary incontinence; enuresis; obstruction; hydronephrosis)
Disorders of the kidneys (eg, pyelonephritis; glomerulonephritis; interstitial nephropathy; renal insufficiency and failure; oliguria, anuria, azotemia, uremia, renal osteodystrophy; hypertensive renal disease; lupus nephritis; inherited disorders)
Traumatic injury
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
13. Disorders of Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Puerperium
Health and Health Maintenance
- Prenatal care (eg, nutrition; prevention of iron deficiency; prevention of vitamin deficiency; Rh immunoglobulin prophylaxis; prenatal diagnosis; teratology, diabetes mellitus, urinary tract infection, ?-fetoprotein, rubella, genital herpes, streptococcal infections)
Assessment of the at-risk pregnancy; risk of preterm labor
Intrapartum care; signs of fetal compromise
Contraception; sterilization; prevention of pregnancy after rape
Mechanisms of Disease
- Placenta, placental dysfunction
Pregnancy and labor, including infection
Postpartum disorders, including infection
Fetus and newborn
Diagnosis
- Pregnancy and labor, including obstetric complications (eg, ectopic pregnancy; spontaneous abortion/septic abortion; hypertension; third-trimester bleeding; hydramnios; preterm labor, premature rupture of the membranes, normal labor; multiple gestation; intrapartum fetal distress/fetal death; maternal mortality; fetal growth and development abnormalities; congenital abnormalities; gestational trophoblastic disease)
Nonobstetric complications of pregnancy (eg, major medical complications and preexisting medical conditions; surgical complications; hyperemesis gravidarum)
Complications of the puerperium (eg, problems with breast-feeding; postpartum hemorrhage; postpartum sepsis; postpartum depression, psychosis; mastitis; venous thromboembolism)
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
14. Disorders of the Skin and Subcutaneous Tissues
Health and Health Maintenance
- Epidemiology and prevention of skin disorders secondary to exposure to the sun; contact dermatitis and drug reactions; decubitus ulcers; dermatophytic skin disorders
Mechanisms of Disease
- Skin disorders, including cancer, infections, and inflammatory disorders
Diagnosis
- Infections (eg, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, chickenpox; cellulitis, carbuncle, abscess, gangrene; dermatophytoses; pilonidal cyst; viral warts; decubitus ulcers)
Neoplasms (eg, squamous cell carcinoma; melanoma; actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma; pigmented nevi; hemangiomas)
Other skin disorders (eg, industrial, occupational, and atopic dermatitis; psoriasis; seborrhea; acne)
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
15. Diseases of the Musculoskeletal System and Connective Tissue
Health and Health Maintenance
- Epidemiology, impact, and prevention of degenerative joint and disc disease
Prevention of disability due to musculoskeletal disorders or infection (eg, osteomyelitis; septic arthritis; Lyme disease; gonococcal tenosynovitis)
Mechanisms of Disease
- Infections
Nerve compressions and degenerative, metabolic, and nutritional disorders
Inherited, congenital, or developmental disorders
Inflammatory or immunologic disorders
Diagnosis
- Infections (eg, osteomyelitis; septic arthritis; Lyme disease; gonococcal tenosynovitis)
Degenerative, metabolic, and nutritional disorders (eg, degenerative joint disease; degenerative disc disease; gout; rickets)
Inherited, congenital, or developmental disorders (eg, congenital hip dysplasia; phocomelia; osteochondritis; slipped capital femoral epiphysis; scoliosis; syringomyelia, dislocated hip in infantile spinal muscular atrophy)
Inflammatory, immunologic, and other disorders (eg, polymyalgia rheumatica; lupus arthritis; polymyositis-dermatomyositis; rheumatoid arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis; bursitis; tendinitis; myofascial pain; fibromyalgia; shoulder-hand syndrome; Dupuytren contracture; Paget disease)
Neoplasms (eg, osteosarcoma; metastases to bone; pulmonary osteoarthropathy)
Traumatic injury and nerve compression and injury (eg, fractures, sprains, dislocations, carpal tunnel syndrome; cauda equina syndrome, low back pain)
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
16. Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders
Health and Health Maintenance
- Diabetes mellitus, including prevention of morbidity and mortality due to complications
Screening (eg, cancer)
Mechanisms of Disease
- Thyroid function
Diabetes mellitus and carbohydrate metabolism
Parathyroid and calcium metabolism
Pituitary and hypothalamic function
Adrenal function
Diagnosis
- Thyroid disorders (eg, nodule; carcinoma; acquired hypothyroidism; thyroiditis; thyrotoxicosis; congenital hypothyroidism; goiter)
Diabetes mellitus (eg, type 1, type 2; ketoacidosis; hyperosmolar coma; chronic complications)
Parathyroid and calcium disorders (eg, hyperparathyroidism; hypoparathyroidism), and hypoglycemia and hyperinsulinism (eg, iatrogenic; insulinoma)
Pituitary, hypothalamic disorders (eg, diabetes insipidus; inappropriate ADH secretion; panhypopituitarism; acromegaly)
Adrenal disorders (eg, corticoadrenal insufficiency; Cushing syndrome; adrenogenital syndrome; hyperaldosteronism; pheochromocytoma)
Heat-related illness
Principles of Management
(With emphasis on topics covered in Diagnosis)
- Pharmacotherapy only
Management decision (treatment/diagnosis steps)
Treatment only
17. Congenital Anomalies
18. Conditions Originating in the Perinatal Period
19. Symptoms, Signs, and Ill-defined Conditions
20. Injury and Poisoning
How is it graded

Well...
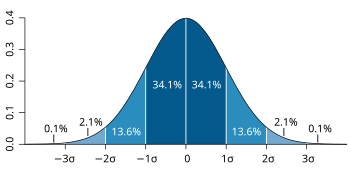
It's graded on a Gaussian curve with a mean of approximately 220 and a standard deviation of approximately 20. This means if you score a 220, you're at the 50th percentile; if you score a 240, you're at 84th percentile; and if you score a 260, you're at the 97th percentile.
When will you do it

August 12th, 2014.
Isn't it impossible to know all that

I agree with you.
Getting 75 to 80% of the questions right on the exam will guarantee you a very high score.
Why are you doing this to yourself

I want to practice medicine in the US.
Why not practice medicine in your country

My country sucks.

How long have you been studying

Five months or so.
What study materials have you used

Various books, videos, lectures, flash cards, and question banks.
I've read the Kaplan Lecture Notes 2014 edition, Master the Board Step 2 CK 2nd ed, Step 2 CK Secrets 3rd ed. I bought the First Aid for the USMLE Step 2 CK, but I don't really like it. I also bought Dr. Fischer's flash cards on Most Likely Diagnosis, Pharmacology, Physical Findings, and Diagnostic Tests. I did the Kaplan Step 2 CK Live Lectures, hence, I didn't watch the video lectures. I've watched several of Kaplan's High-Yield Video Lectures, nonetheless. Finally, I've been doing Kaplan and USMLEWorld question banks.
What's the point of this thread

Well...
I had a similar thread for my USMLE Step 1. I get bored while studying. Constantly updating what I've been doing encourages me to keep studying. Also, all the warm comments from the forum members are a great deal of comfort to me. In other words, it helps to cheer me up. :cheers: :toot: :!:

Is there something you want us to do

Yes! Wish me luck!

